In this 1D example, a porous solid saturated with fluid is compressed
by a force ![]() on the solid phase. The length of the test specimen is
on the solid phase. The length of the test specimen is
![]() , plane strain conditions hold, the Young's modulus is
, plane strain conditions hold, the Young's modulus is ![]() , Poisson's ratio
is
, Poisson's ratio
is ![]() , permeability
, permeability ![]() , width of test specimen
, width of test specimen ![]() , thickness
, thickness ![]() ,
area
,
area ![]() . Some non-dimensional variables are introduced
. Some non-dimensional variables are introduced
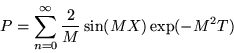
Now we choose: ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() .
Thus, for
.
Thus, for ![]() at
at ![]() we should find
we should find ![]() .
The numerical analysis (5 elements, time step size 0.01) gives
.
The numerical analysis (5 elements, time step size 0.01) gives ![]() .
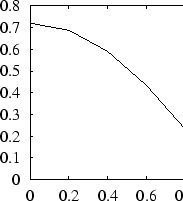
The pressure distribution at
.
The pressure distribution at ![]() is given below
is given below