A rectangular piece of material (size 1 by 1; Young's modulus ![]() )
is rubbed against a solid wall. In this example, we will analyze the stresses
and temperature profile caused by frictional heat generation.
The free edges of the material are prescribed to have temperature 0.
)
is rubbed against a solid wall. In this example, we will analyze the stresses
and temperature profile caused by frictional heat generation.
The free edges of the material are prescribed to have temperature 0.
The deformed mesh (with 16 quadratic elements) at time ![]() looks like:
looks like:
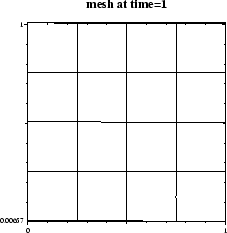
Initially the right edge of the material did penetrate the solid wall
over a distance ![]() , but the contact algorithm did eliminate this
penetration.
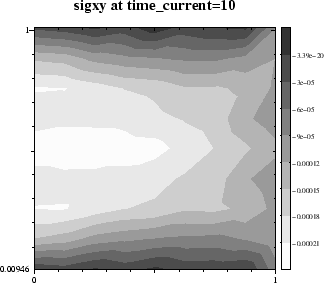
This resulted in a normal stress -sigxx of about size
, but the contact algorithm did eliminate this
penetration.
This resulted in a normal stress -sigxx of about size ![]() .
The normal stress causes a frictional stress -sigxy of about size
.
The normal stress causes a frictional stress -sigxy of about size ![]() at the interface between material and solid wall, due to a friction coefficient
of
at the interface between material and solid wall, due to a friction coefficient
of ![]() :
:
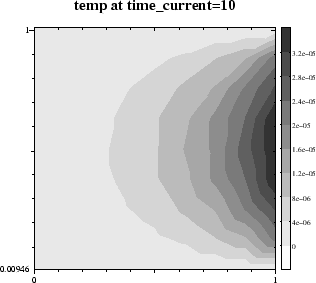
This frictional stress, in turn, causes frictional heat generation. The stationary temperature profile is plotted below: